March 26, 2021: On May 29, 1919, the Moon slid in front of the sun and forever altered our understanding of spacetime. It was “Einstein’s Eclipse.” Using the newly-developed theory of relativity, the young German physicist predicted that the sun’s gravity should bend starlight–an effect which could be seen only during a total eclipse. Some of the greatest astronomers of the age rushed to check his prediction.
More than 100 years later, Petr Horálek (ESO Photo Ambassador, Institute of Physics in Opava) and Miloslav Druckmüller (Brno University of Technology) have just released a stunning restoration of the photo that proved Einstein right:

The original picture was taken in May 1919 by astronomers Andrew Crommelin and Charles Rundle Davidson, who traveled from the Greenwich Observatory in London to the path of totality in Sobral, Brazil. They were part of a global expedition organized in part by Sir Arthur Eddington, who wanted to test Einstein’s strange ideas. Glass photographic plates from the expedition were typical of early 20th century astrophotography, colorless and a little dull.
“Our restoration shows how the eclipse would have been recorded today–a magnificent sight,” says Horálek. “The astronomers in Brazil must have been amazed when they saw the giant prominence with their unaided eyes.”

Horálek got the idea for this restoration in 2019 when he saw a partially restored image released by the ESO (European Southern Observatory) to celebrate the 100th anniversary of the eclipse. A scan of the original plate was provided by the Heidelberg Digitized Astronomical Plates project … and then the real work began.
“I started by manually removing scratches and specks of dust from the copied plate,” says Horálek. “There were dozens of them, and the whole process took about 50 hours of work.”
Next, Horálek applied Noise Adaptive Fuzzy Equalization (NAFE) software to sharpen the remaining details. NAFE was developed by Prof. Druckmüller to enhance images from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory. It worked marvelously on the old eclipse, revealing delicate streamers and hints of a dipole structure in the sun’s corona.
Finally, he added color. “I created a palette to make the image as natural as possible. The sun’s corona is white because it is sunlight scattered by free electrons. The prominence has that special red color (H-alpha) which hydrogen makes in the sun’s atmosphere. Once these two colors were fixed, the dark-blue hue of the background sky emerged naturally. Voilà!–a modern view of Einstein’s eclipse.”
Meanwhile, back in 1919, the eclipse was a sensation. Eddington measured the positions of stars near the sun during the eclipse. (Two of them, 65 and 67 Tauri, may be found in the bottom right of the restoration.) They were displaced just as Einstein predicted. Spacetime really was a fabric that could be stretched.
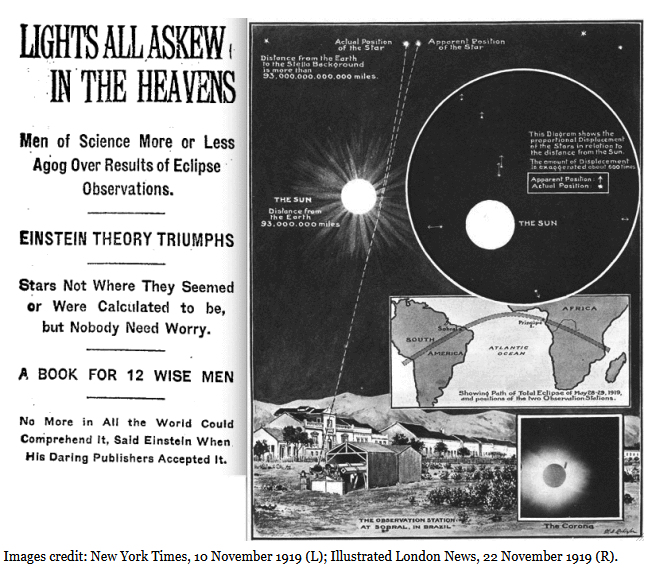
The result was splashed across the front pages of most major newspapers. It made Einstein and his theory of general relativity world-famous. Einstein has been quoted as describing his reaction if general relativity had not been confirmed by Eddington and Dyson in 1919: “Then I would feel sorry for the dear Lord. The theory is correct anyway.”
“2021 is the 100th anniversary of Einstein’s Nobel Prize,” notes Horálek. “This photo is our way of paying tribute to his work.”
Full credit: ESO/Landessternwarte Heidelberg-Königstuhl/F. W. Dyson, A. S. Eddington, & C. Davidson, P. Horálek/Institute of Physics in Opava, M. Druckmüller.
Reblogged this on Tallbloke's Talkshop and commented:
Some real science to remember.
LikeLike
Fantastic reproduction!
LikeLike
How many arc seconds were the images of the stars deflected?
How many arc seconds were the star images away from the image of the eclipsed sun?
During the August 2017 total solar eclipse I captured images of the sun and the star Regulus.
How much was the image of Regulus deflected by the sun’s gravity?
LikeLike
According to NASA, Regulus at its distance from the edge of the sun was deflected by only 1/3rd of an arcsecond.
LikeLike
PS Search this web page for “Regulus” https://eclipse2017.nasa.gov/testing-general-relativity
LikeLike
Do any first hand accounts of totality mention the incredibly large prominence?
LikeLike
Ooops – missed that it was mentioned in the article! Never mind.
LikeLike